Graphical abstract
Introduction
Advanced therapies represent a continuous challenge not only for the improvement of the pathological conditions of millions of patients, but also for the development of innovative high-tech systems that allow to produce in accordance with the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) safe and effective drugs within “cell factories”.
The development of new generation technological solutions arises from the need to simplify the work-flow of even very complex processes in closed and automated systems.
Regulatory Aspects:
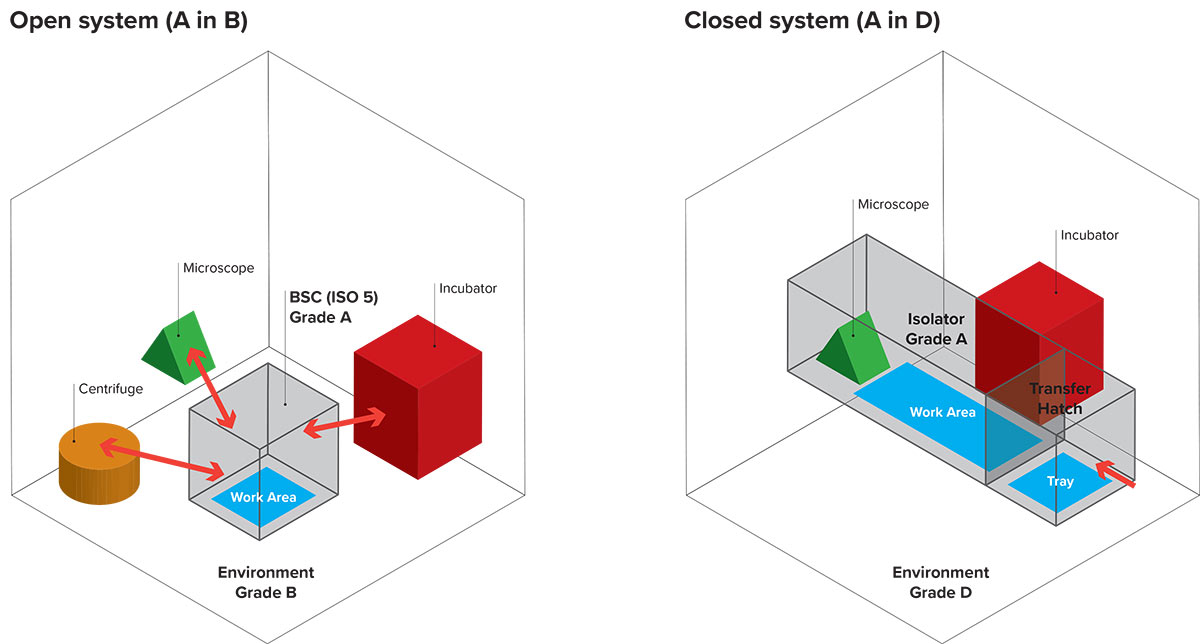
Why choose a closed system (Isolator) instead of an open system (Clean Room) in a cell factory?
The physical separation of the product / operator allows a greater degree of safety for both the drug and the operator. In EUDRALEX Vol. 4, Annex 1 2020, it specifically says in paragraph 4.3: “[…] isolators are beneficial in assuring the required conditions and minimizing the microbial contamination associated with direct human interventions in the critical zone. Their use should be considered in the CCS. Any alternative approaches to the use of […] isolators should be justified. ” So if for a given system, the choice was to use a clean room instead of an isolator, this alternative approach should be justified. Operating Procedures:
The possibility of installing the closed system in a class D (A in D) allows to simplify the operating procedures relating to personnel flow, dressing, validations, infrastructure complexity compared to the use of Grade A Safety Cabins (ISO 4.8) inside Grade B cleanrooms (open system or A in B)
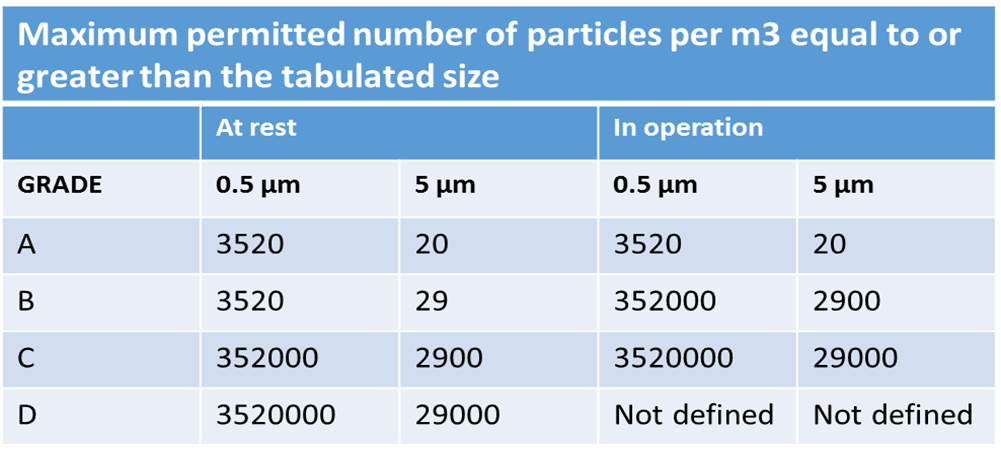
Figure 1 Clean rooms Grade and number of particles
The isolators: an eco-sustainable choice A closed system allows an economic saving of the facility’s operating costs of the order of 70% compared to an open system. The savings were estimated by comparing two systems, respectively, a Grade B clean room with Safety Cabinets for Class 4.8 (A in B) and a Grade D Clean Room in which an isolator with a Grade work area was installed. A (A in D), for the production of ATMPs. The energy consumption, which in the case of the clean room A in B is onerous given the complexity of the ventilation systems to guarantee the zones in Grade D, C and B respectively, are greatly reduced for the management of only the Grade D zone with an isolator. In addition to impacting on the operators, the dressing is a non-negligible expense item which in the case of the use of an insulator is reduced by more than half, since the suit is not necessary. In terms of validation, the savings for the qualification of a smaller system is certainly another not negligible aspect. The maintenance of a clean room over time remains of high economic impact which does not happen in the case of a closed system.
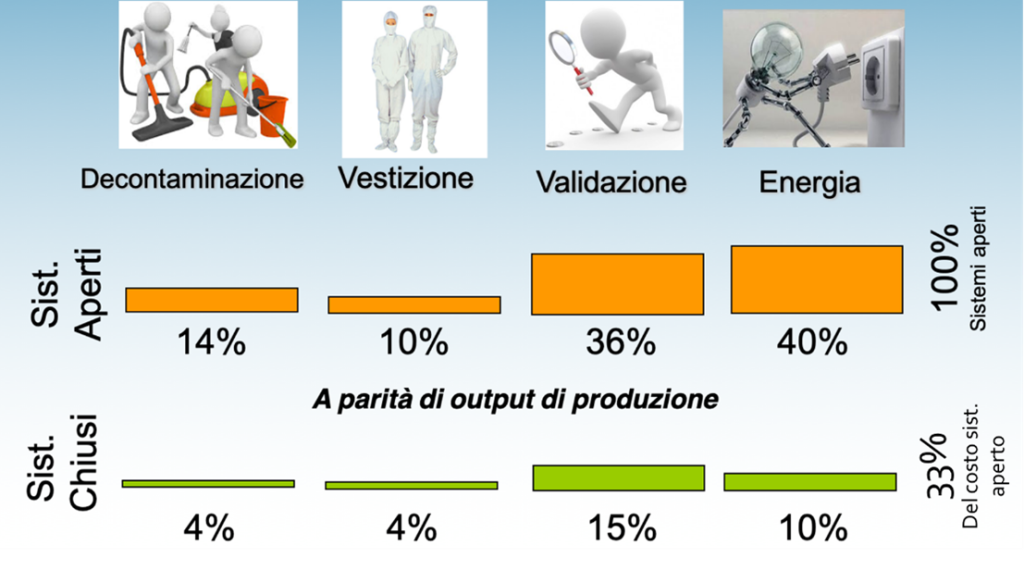
Figure 2 Savings achieved with the use of closed systems compared to open systems.
Cleaning operations are simplified and faster using H2O2 vapors and manual cleaning is streamlined. The same applies to the validation and requalification operations. Cleaning operations in cells, factories constitute a real process to be validated and applied according to the regulations of Annex 1. They are operations that are entrusted to appropriately trained specialized personnel. A closed system is 100% sterilizable with hydrogen peroxide in a completely automated way. Manual cleaning is also simplified given the possibility of reaching every point of the work area by the same operators who can thus sanitize the internal space of the insulator at the end of the day.
Other Closed Systems Bioreactors
The need to standardize these production processes has the ultimate goal of making advanced cell therapy products not only safer, but also of improving their efficiency in production. The automated system for cell culture NANT 001 (VivaBioCell SpA) presented in the article allows the expansion of different cell populations in a closed and aseptic environment, in compliance with the guidelines of Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP), lowering many of the possible risks arising from manual processing, ensuring constant monitoring and traceability of processes. The cost model developed internally by VivaBioCell on the basis of a production process of an advanced cell-based therapy.
Recent Articles
- Cell therapy based on neuronal precursors for the treatment of multiple sclerosis 10 January 2023
- How to Improve the Sustainability of Advanced Therapies: The Case of Strimvelis 24 November 2022
- FDA reorganization: a “Super Office” to manage the increasing cell and gene therapy workload 3 November 2022
- GMP Cleanliness Classifications: Deciphering the Differences and Requirements among Grades 12 September 2022
- How to Overcome the Most Common Issues in the GMP-Compliant Culturing of Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Isolation and Automatization 30 August 2022